AI Virtual Assistants and chatbots are both examples of conversational agents that can interact with users via text or speech using Natural Language Understanding (NLU). However, there are some key differences between them:
Scope of interaction
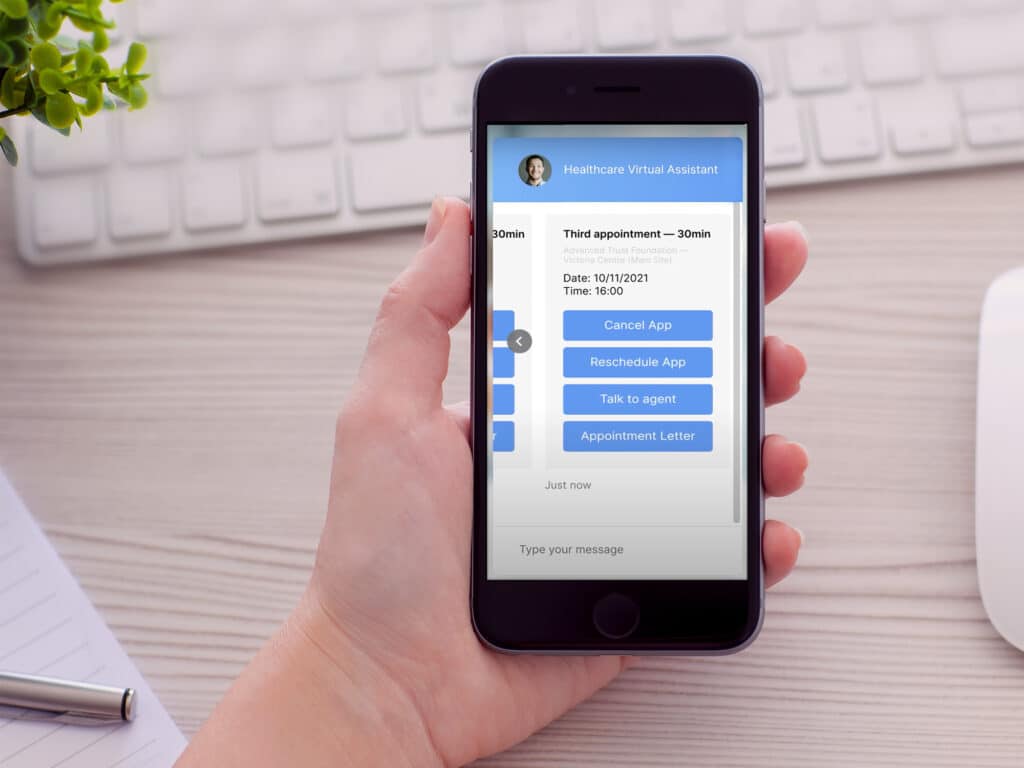
Virtual Assistants are designed to be more advanced by handling more complex and personalised interactions with users, while chatbots typically focus on specific tasks or answering simple queries. For example, a Virtual Assistant might be able to help a user book or cancel an appointment, check current appointments, whereas a chatbot might be limited to answering frequently asked questions or providing basic customer support.
Natural Language Understanding
Virtual Assistants typically use more advanced NLP technologies to understand user requests and generate appropriate responses. This allows them to understand context and carry out more complex interactions. Chatbots, on the other hand, may rely on simpler rule-based approaches or pre-defined scripts to respond to user inputs. The NLU engine that supports Virtual Assistants is built and optimised to answer queries in a more flexible and personalised way by taking the full context of a conversation into account.
Integration with other systems
Virtual Assistants are often integrated with other systems and databases to provide more comprehensive services. For example, a Virtual Assistant for the NHS will be able to access electronic patient records and manage bookings online, while a chatbot might only be able to provide information on appointments.
Personality and branding
Virtual Assistants are often designed to have a distinct personality and branding that reflects the company or product they represent. This can help to build a relationship with users and create a more engaging user experience. Chatbots, on the other hand, are often designed to be more functional and utilitarian, with less emphasis on personality or branding.
Virtual Assistants can orchestrate patient outreach whilst simultaneously automating repetitive tasks. They’re a clever combination of ‘smart chatbot’, robotic process automation (RPA) and AI for healthcare, all focused upon NHS workflows. An NHS Virtual Assistant can be pre-trained with hundreds of intentions relevant to a Trust’s patients. Thanks to its AI component, the Virtual Assistant constantly learns from its own feedback and provides robust analytics supporting deep insight.
Why should the NHS care?
Increased choice for patients
Because Virtual Assistants have the potential to improve patient outcomes and reduce costs. They provide patients with choice when communicating with their Trust and improve access to personalised care and support enabling healthcare providers to free up precious time for staff to focus on more complex tasks. Virtual Assistants can also be used to improve patient engagement and education and can help patients better manage their health conditions.
Improved access to healthcare
In addition, Virtual Assistants can help reduce waiting times and improve access to healthcare services. Patients can use them to schedule appointments, request prescriptions, or get answers to their questions, without having to wait on hold or visit a clinic in person.
Enhanced quality of care
Data analytics can also be used to optimise Virtual Assistant interactions with patients, by identifying which types of questions and responses are most effective at achieving desired outcomes. This can help improve the overall quality of care provided by Virtual Assistants and ensure that patients receive the support and guidance they need.
Data gathering and analytics
Moreover, Virtual Assistants can be used to collect data on patient experiences and satisfaction with healthcare services. This data can be analysed using data analytics tools to identify areas where improvements can be made, such as reducing wait times or improving the quality of care provided.
Overall, Virtual Assistants and data analytics are complementary tools that can be used to improve healthcare services and patient outcomes. The NHS should consider the potential benefits of Virtual Assistants to provide more personalised, efficient, and effective care to patients, while gaining new insights into the needs and preferences of patients.
Interested in finding out how your NHS Trust can transform patient communications through the use of AI-powered Virtual Assistants? Book a chat with us today.